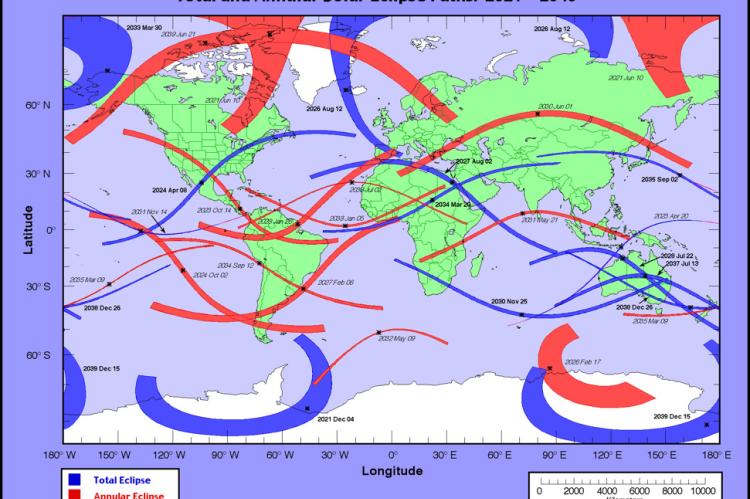
Geography of the Solar Eclipse
No two eclipses are exactly the same as viewed from here on Earth. Why are they always different? The location, path and timing of an eclipse is the result of many factors. Most important is that the Moon’s shadow reaches Earth during a lunar new Moon phase when the Earth-Moon-Sun alignment is just right.
The path of a solar eclipse, or the Moon’s shadow, on Earth’s sunlit side matches the motion of the Moon as it moves in orbit around Earth. The shape of the shadow and how fast it moves determines the width of the path and length of totality along the eclipse swath.
The figure in the corner depicts the variation in location and size of the path of a solar eclipse. The curvature of the eclipse path is from the projection of a mostly round Earth onto a flat map.
Every eclipse is different and unique. During an eclipse, factors such as variation in Sun angle, Earth’s curvature, the tilt of its axis and even lunar limb topography influence the shape and size of the Moon’s shadow,…